tryhackme - Attacktive Directory

Table of Contents
Room: Attacktive Directory
Difficulty: Medium
Room created by Spooks
Task 1 Intro Deploy The Machine
Accessing Attacktive Directory: visit this link, follow the walkthrough and connect to the tryhackme network.
Task 2 Intro Setup
- Installing Impacket
Whether you’re on the Kali 2019.3 or Kali 2021.1, Impacket can be a pain to install correctly. Here’s some instructions that may help you install it correctly!
First, you will need to clone the Impacket Github repo onto your box. The following command will clone Impacket into /opt/impacket:
git clone https://github.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket.git /opt/impacket
To install the Python requirements for Impacket:
pip3 install -r /opt/impacket/requirements.txt
Once the requirements have finished installing, we can then run the python setup install script:
cd /opt/impacket/ && python3 ./setup.py install
After that, Impacket should be correctly installed now and it should be ready to use!
If you are still having issues, you can try the following script and see if this works:
Credit for proper Impacket install instructions goes to Dragonar#0923 in the THM Discord <3
- Troubleshooting
If you are having issues with Impacket, reach out to the TryHackMe Discord for help!
Task 2.1 - Install Impacket, Bloodhound and Neo4j
No Answer Needed
We don’t need Bloodhound and Neo4j to complete this room, so I skipped the installation for those, but if you want to install those as well, follow the instruction given here.
Task 3 Enumeration Welcome to Attacktive Directory
Enumeration
Basic enumeration starts out with an nmap scan. Nmap is a relatively complex utility that has been refined over the years to detect what ports are open on a device, what services are running, and even detect what operating system is running. It’s important to note that not all services may be deteted correctly and not enumerated to it’s fullest potential. Despite nmap being an overly complex utility, it cannot enumerate everything. Therefore after an initial nmap scan we’ll be using other utilities to help us enumerate the services running on the device.
For more information on nmap, check out the nmap room.
Notes: Flags for each user account are available for submission. You can retrieve the flags for user accounts via RDP (Note: the login format is spookysec.local\User at the Window’s login prompt) and Administrator via Evil-WinRM.
Task 3.1 - What tool will allow us to enumerate port 139/445?
REDACTED
Command to do all simple smb enumeration with enum4linux:
Let’s read a little bit about the ports mentioned in the task:
- Port 139: NetBIOS stands for Network Basic Input Output System. It is a software protocol that allows applications, PCs, and Desktops on a local area network (LAN) to communicate with network hardware and to transmit data across the network.
- Port 445: While Port 139 is known technically as ‘NBT over IP’, Port 445 is ‘SMB over IP’. SMB stands for ‘Server Message Blocks’. Server Message Block in modern language is also known as Common Internet File System. The system operates as an application-layer network protocol primarily used for offering shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and other sorts of communications between nodes on a network.
For instance, on Windows, SMB can run directly over TCP/IP without the need for NetBIOS over TCP/IP. This will use, as you point out, port 445. On other systems, you’ll find services and applications using port 139. This means that SMB is running with NetBIOS over TCP/IP. [information source]
I use smbclient instead of enum4linux for smb enumeraion, let’s enumerate:
smbclient -N -L \\\\10.10.95.227
-L flag to to list shares and -N flag to set NoPassword and try anonymous login attempt.
OK, got nothing here with anonymous login.
Lets run our nmap scan (nmap -T4 -sC -sV <IP>) to see what we have on this machine:
I usually run all port nmap scan as well (nmap -T4 -p- <IP>) so that I don’t miss anything:
Looks like there’s nothing interesting in the second scan.
Task 3.2 - What is the NetBIOS-Domain Name of the machine?
REDACTED
Look closly in the results of first nmap scan.
Task 3.3 - What invalid TLD do people commonly use for their Active Directory Domain?
REDACTED
Read this to look for your answer or google the question.
TLDR: .local is reserved by ICANN, no external DNS server will resolve this domain.
Task 4 Enumeration Enumerating Users via Kerberos
- Introduction
A whole host of other services are running, including Kerberos. Kerberos is a key authentication service within Active Directory. With this port open, we can use a tool called Kerbrute (by Ronnie Flathers @ropnop) to brute force discovery of users, passwords and even password spray!
- Enumeration
For this box, a modified User List and Password List will be used to cut down on time of enumeration of users and password hash cracking. It is NOT recommended to brute force credentials due to account lockout policies that we cannot enumerate on the domain controller.
Task 4.1 - What command within Kerbrute will allow us to enumerate valid usernames?
REDACTED
Run /path/to/binary/kerbrute_linux_amd64 --help
Task 4.2 - What notable account is discovered? (These should jump out at you)
REDACTED
Task 4.3 - What is the other notable account is discovered? (These should jump out at you)
REDACTED
Task 5 Exploitation Abusing Kerberos
- Introduction
After the enumeration of user accounts is finished, we can attempt to abuse a feature within Kerberos with an attack method called ASREPRoasting. ASReproasting occurs when a user account has the privilege “Does not require Pre-Authentication” set. This means that the account does not need to provide valid identification before requesting a Kerberos Ticket on the specified user account.
- Retrieving Kerberos Tickets
Impacket has a tool called “GetNPUsers.py” that will allow us to query ASReproastable accounts from the Key Distribution Center. The only thing that’s necessary to query accounts is a valid set of usernames which we enumerated previously via Kerbrute.
Task 5.1 - We have two user accounts that we could potentially query a ticket from. Which user account can you query a ticket from with no password?
REDACTED
Task 5.2 - Looking at the Hashcat Examples Wiki page, what type of Kerberos hash did we retrieve from the KDC? (Specify the full name)
REDACTED
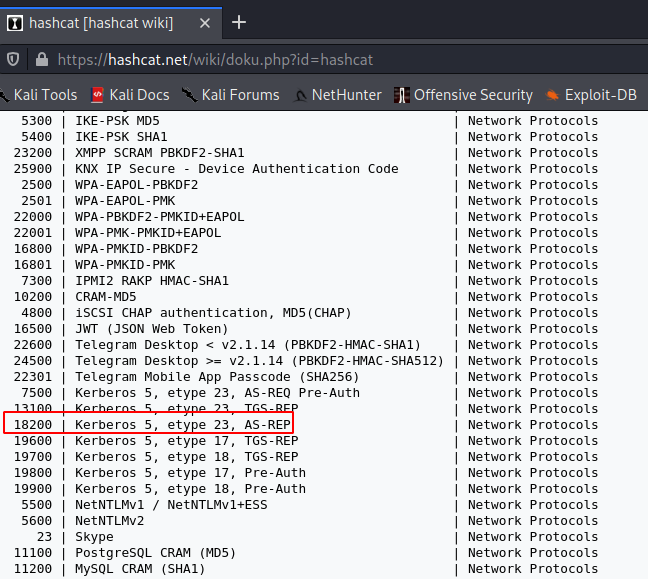
Task 5.3 - What mode is the hash?
REDACTED
Task 5.4 - Now crack the hash with the modified password list provided, what is the user accounts password?
REDACTED
hashcat -m 18200 -a 0 /root/dir/tryhackme/attactive_directory_redo/saved.hash /root/dir/tryhackme/attactive_directory_redo/passwordlist.txt --force
Task 6 Enumeration Back to the Basics
Enumeration
With a user’s account credentials we now have significantly more access within the domain. We can now attempt to enumerate any shares that the domain controller may be giving out.
Task 6.1 - What utility can we use to map remote SMB shares?
REDACTED
I have mentioned this tool before we ran the nmap scan.
Task 6.2 - Which option will list shares?
REDACTED
Task 6.3 - How many remote shares is the server listing?
REDACTED
Now that we got a username and a password, we can enumerate the shares again using obtained credentials:
Task 6.4 - There is one particular share that we have access to that contains a text file. Which share is it?
REDACTED
Task 6.5 - What is the content of the file?
REDACTED
Awesome, we got credentials:
Task 6.6 - Decoding the contents of the file, what is the full contents?
REDACTED
Task 7 Domain Privilege Escalation Elevating Privileges within the Domain
Let’s Sync Up!
Now that we have new user account credentials, we may have more privileges on the system than before. The username of the account “backup” gets us thinking. What is this the backup account to?
Well, it is the backup account for the Domain Controller. This account has a unique permission that allows all Active Directory changes to be synced with this user account. This includes password hashes
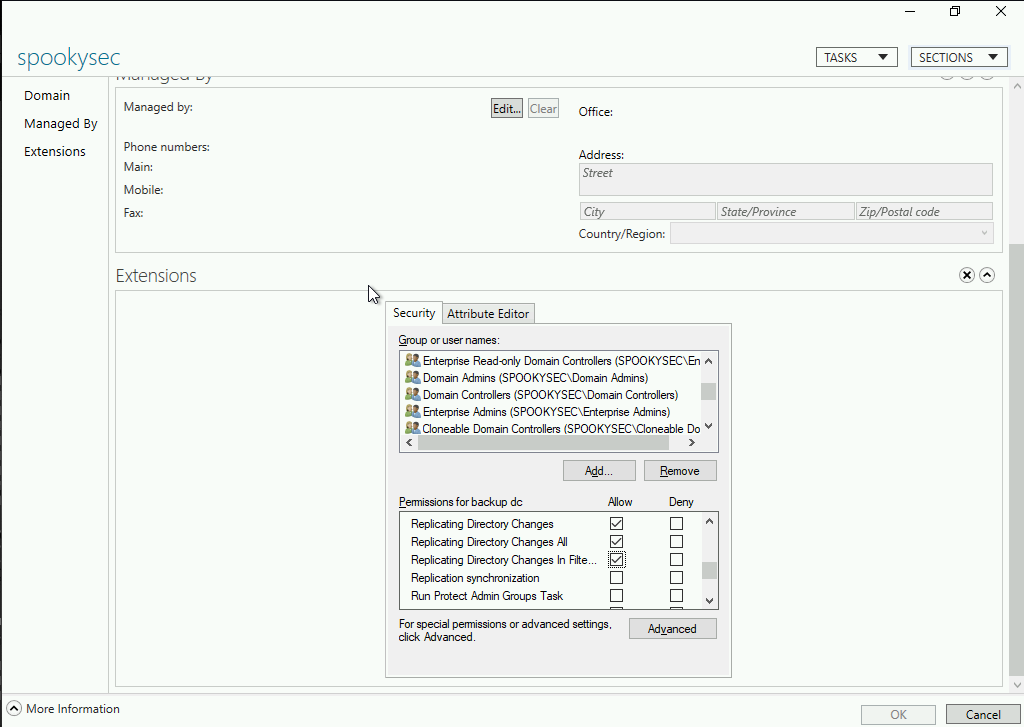
Knowing this, we can use another tool within Impacket called secretsdump.py. This will allow us to retrieve all of the password hashes that this user account (that is synced with the domain controller) has to offer. Exploiting this, we will effectively have full control over the AD Domain.
Task 7.1 - What method allowed us to dump NTDS.DIT?
REDACTED
Carefully read the secretsdump.py scan results.
Task 7.2 - What is the Administrators NTLM hash?
REDACTED
Task 7.3 - What method of attack could allow us to authenticate as the user without the password?
REDACTED
Which method of attack is used when you have a username and a NTLM hash to authenticate?
Task 7.4 - Using a tool called Evil-WinRM what option will allow us to use a hash?
REDACTED
Run Evil-WinRM --help
Task 8 Flag Submission Flag Submission Panel
Flag Submission Panel
Submit the flags for each user account. They can be located on each user’s desktop.
If you enjoyed this box, you may also enjoy room creators blog post!
Task 8.1 - svc-admin
REDACTED
Task 8.2 - backup
REDACTED
Task 8.3 - Administrator
REDACTED
I hope you enjoyed and got something usefull from this writeup, happy hacking 🔥